The financial ecosystem is rapidly evolving, and several digital money concepts have emerged in recent years that are making it easier to move away from cash. Also, the pandemic has naturally helped to increase the use of digital currencies since more purchases are being done online.
There has been an increasing interest in cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin throughout the years working on the distributed blockchain technology. Because of their decentralized and less regularized nature, the virtual currencies are gaining great popularity. Some regard their growth as a potential threat to the traditional banking system, under the jurisdiction and supervision of the regulatory authorities in a country, including the central bank.
Many top central banks across the world can't manage the surge and impact of such cryptocurrencies, but they're working on or planning to introduce their own equivalents. These controlled cryptocurrencies are known as Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC), operated by a nation's financial authority and central banks. According to a survey conducted by the Bank of International Settlements, 86% of central banks are exploring or experimenting with CBDCs, and a fifth of the global population might be utilizing CBDCs in three years.
Understanding CBDC
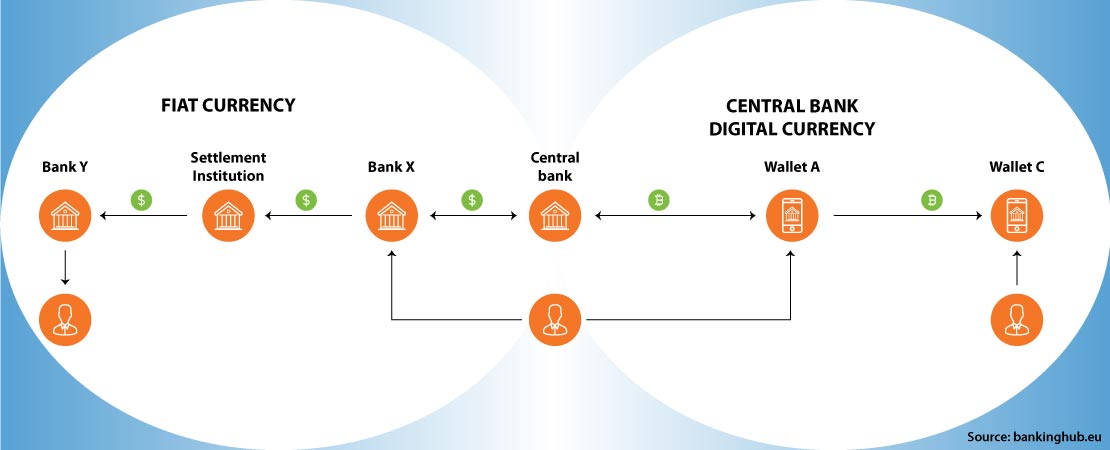
CBDC, issued by the central bank, is digital money. It functions as a token or account-based solution. CBDCs based on tokens can be transacted like cash. People have the digital wallet tokens or ‘digital cash’, that comes with token validity.
Account-based CBDCs act like digital bank accounts, however they are held by the central bank instead of a commercial bank. When creating a CBDC account, it is important to identify both the payer and the payee and ensure that the payer has enough funds to perform the transaction.
Difference between CBDC and Cryptocurrency
Fundamental similarities between Cryptocurrencies and CBDC may be seen easily. Cryptocurrencies have a common characteristic of decentralized settlement without the necessity for a trustworthy counterpart, ownership based on encryption keys rather than on accounts, and the ability to change validity via smart contracts. A CBDC with all these features can be designed, making both of them quite comparable.
The value of CBDCs is frequently linked to currency value, and its supply is directly controlled by the central bank. On the other hand, the value of cryptocurrencies is decided by their supply and demand, which leads to extreme volatility.
Resolving difficult mathematical equations in order to mine a cryptocurrency is necessary for tokens and transactions to be generated and distributed. However, central banks can settle CBDC transactions and transfer the monetary value to the public, e.g., exchange physical money for digital money. In the future CBDCs could be more acceptable as digital currencies than private cryptocurrencies for emerging markets, but only if genuine cryptocurrencies are widely circulated.
Impact of CBDC
The CBDC could be critical to preserve monetary sovereignty. If people move to digital currencies via cryptocurrencies, governments may lose control over their currency policies. Cryptocurrencies also pose a direct threat for the central banks in maintaining financial stability and managing inflation. A CBDC would permit citizen-driven shifts while maintaining control of the central bank.
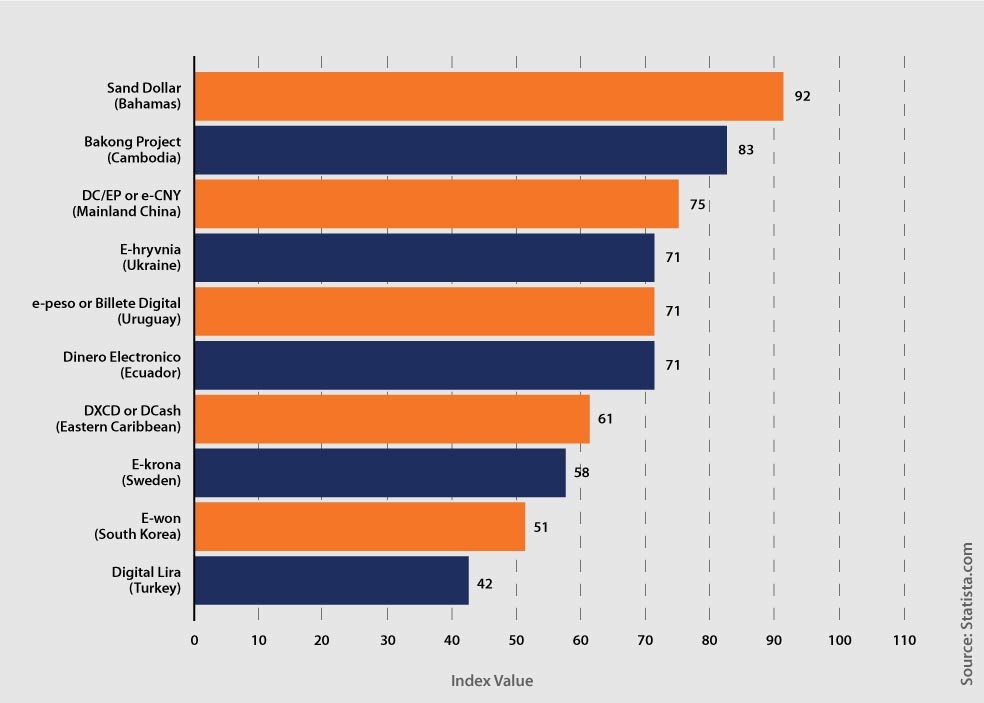
As of December 2020, China ranks third in the world in terms of the development of its retail CBDC. China's retail efforts in cryptocurrencies, allegedly planning to introduce its e-CNY digital currency during the 2022 Beijing Winter Olympics, were placed behind Cambodia and the Bahamas in an index published in early 2021.
The Retail CBDC Projects as of 2020
A CBDC is also capable in improving financial inclusion in developing nations. High commissions and no deposit insurance in countries with less established financial systems mean that some people opt out of financial services. Since CBDC deposits are threat-free and generally come with little to no expenses, more people may prefer to use financial services.
The Way Forward
In order to secure the privacy of the user, to prevent fraud, and protect users’ data, and systems against security breaches, CBDC platforms and apps require new-age technology for development. Whatever the central bank decides to do, it is evident that the CBDCs will emerge and change the payment system ecosystem in several nations in a few years. CBDCs can make banking more accessible to a wider range of customers by allowing them to engage in the economy without requiring a bank account. Customers can be their own bank by managing their own keys, storing their money in an application, or .
Panamax offers a Banking Suite equipped with unique features and end-to-end solutions to enable banks and financial institutions provide a comprehensive digital banking experience to their customers. Our consumers benefit from a secure financial ecosystem that is underpinned by considerable research and a three-decade history of redefining financial security.
Related Blogs
Digital Banking: Enabling Growth in the New Normal
5 Key Aspects Required in a Digital Banking Platform